Night vision technology has transformed how we see in the dark, vital for military, security, and outdoor use. The type of night vision you choose can also make a difference. This brings us to the ongoing debate in night vision community: green phosphor vs. white phosphor night vision.
In this detailed guide, we’ll explore the world of night vision technology, breaking down the science behind green and white phosphor, comparing the pros and cons, and bring some clarity to this ongoing debate.
How Night Vision Works
Traditional night vision devices use optoelectronic image enhancement technology. This technology uses optical lenses and a special electronic vacuum tube to capture and amplify the visible light that is reflected off nearby objects:
- Light collection: The device gathers dim visible light, along with some light from the low end of the infrared spectrum, through the objective lens. This light is comprised of small particles called photons.
- Image intensification: The light enters an image intensifier tube where photons strike a photocathode. The photocathode converts photons into electrons.
- Electron amplification: The electron flow is accelerated and multiplied through a microchannel plate (MCP). This process amplifies the electric signal several thousand times over.
- Image formation: The accelerated electrons hit a phosphor screen at the end of the tube, causing it to glow and form a visible image.
What Is a Night Vision Phosphor Screen?
It’s a layer of phosphor on a piece of glass that is used to create an image. This material emits light when hit by electrons, creating a visible image. The color of the image depends on the type of phosphor-coating.
- Green Night Vision Devices
Originally, night vision was done in green phosphor, as human eyes are most sensitive to green light under low-light conditions. This natural sensitivity means that green light appears brighter to us, allowing for better detection of contrast and details in the dark.
- White Night Vision Devices
White phosphor is a newer adaptation that displays images in shades of black, white, and gray. Although invented quite a long time ago in the late 20th century, it appeared as a newer technology in the last decade.
Green vs. White Phosphor Night Vision: Similarities and Differences
The first thing to note about the similarities between white and green phosphors is that both are enhancers of night vision. They can be integrated into devices like sniper scopes, binoculars, and goggles.
Another thing to mention about the two regarding similarities is that both function with low light, and won’t work in blacked-out places. Thermal night vision detectors are better alternatives in complete darkness.
- Advantages Of Using Green Phosphor
- Reliability: For more than four decades, green phosphor has been the industry standard. This technology has been widely tested and proven effective, making it a trusted choice for most applications.
- Cost-Effective: Generally, devices equipped with green phosphor are less expensive than their white phosphor counterparts, providing a good balance of performance and affordability.
- Human Eye Sensitivity: The human eye is more sensitive to green light. This sensitivity means that green phosphor has an advantage in identifying objects and individuals in low-light scenarios.
- Disadvantages of Using Green Phosphor
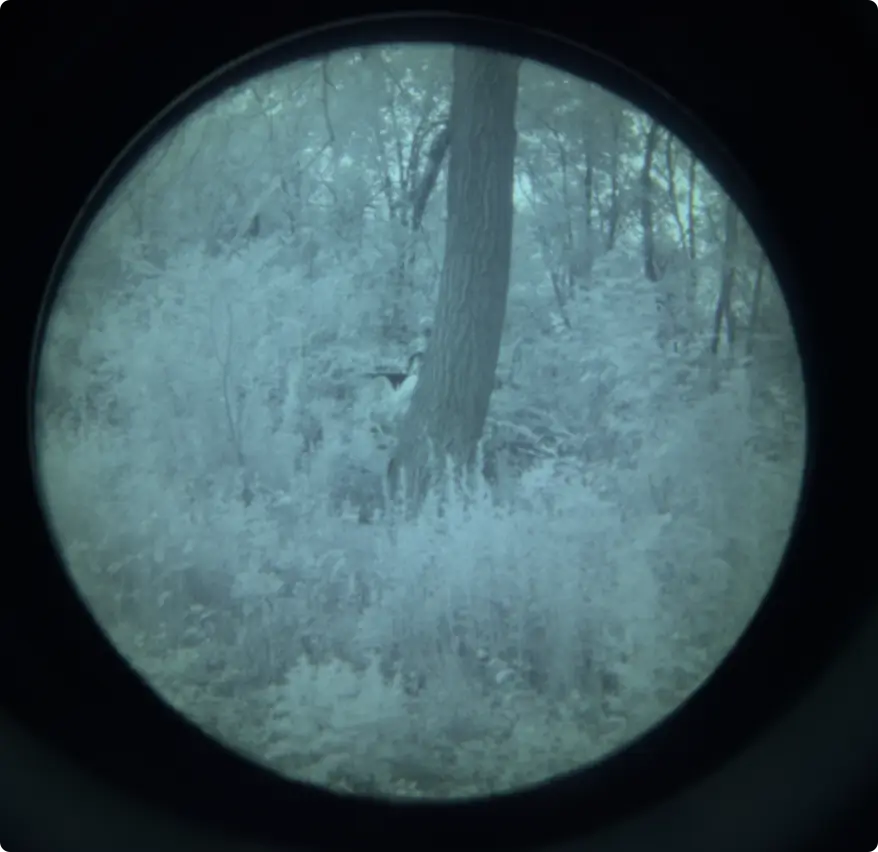

- Lower Image Clarity: Green phosphor displays generally have lower contrast and detail compared to white phosphor. This can make it harder to distinguish fine details, especially in complex or cluttered environments.
- Less Natural Viewing Experience: The green-tinted image doesn’t mimic natural vision, which can make it more difficult for users to adapt or identify objects quickly. White phosphor, with its grayscale image, offers a more lifelike experience.
- Eye Strain Over Time: While green light is less fatiguing than other colors, prolonged use can still lead to eye strain.
- Advantages Of Using White Phosphor
- Improved Contrast: White phosphor presents images in neutral black and white shade, which resembles natural vision more closely than green phosphor.
- Improved Clarity: The grayscale imagery provided by white phosphor allows for enhanced contrast between light and dark areas, offering sharper details and making it easier to identify targets or objects in complex environments.
- Reduced Eye Strain: White phosphor mimics daylight-like vision, it tends to cause less eye fatigue over long periods of use.
- Disadvantages of Using White Phosphor
- Higher Cost: White phosphor night vision devices tend to be more expensive than green phosphor models, which may be a barrier for some users.
- Power Consumption: White phosphor devices often have higher power requirements, necessitating more frequent battery changes or the need for additional power supplies.
Which do I choose: Green Phosphor or White Phosphor Night Vision?

The discussion surrounding green phosphor and white phosphor devices is constantly evolving with advancements in the field. Each phosphor type presents distinct advantages and drawbacks, making the decision largely dependent on the user’s specific needs and context.
Green phosphor has been a reliable choice for decades, known for its dependable performance, good contrast, and affordability. It remains a strong option for many standard applications, especially for users who are accustomed to its characteristics and performance.
White phosphor, on the other hand, represents the forefront of night vision technology. With its superior image quality, improved depth perception, and natural grayscale visuals, it offers significant advantages in high-stakes situations.
When choosing night vision goggles, it’s important to take into account your mission requirements, budget limitations, user experience, and practical considerations like power consumption and availability. By thoughtfully assessing these aspects, user can make a choice that aligns best with their needs. If you need a bit of additional information on this topic, check out our comprehensive night vision products page for specs info.


















Comments